Vacuum fluctuations.
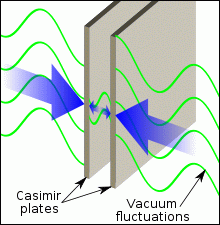
The pressure of the vacuum fluctuations on the parallel plates. The static Casimir effect.
| Sergey B. Alemanov http://alemanow.narod.ru alemanow@mail.ru | |
|
Hubble's quantum law
vn = nH0 (Quantum law of the cosmological redshift) A report in the Moscow State University (13.03.2013, 18.10.2013), Prokhorov General Physics Institute (29.01.2014), Moscow Aviation Institute (29.05.2015), RUDN University (28.04.2016). Published in the «Engineering Physics» (No. 3, 2014). |
|
Hubble's law, as presented in quantum form, allows exact calculation of the cosmological redshift for galaxies at any distance. For example, the distance to galaxies, as calculated on the basis of the contemporary method of "standard candles" (Nobel Prize 2011) mismatches the one calculated on the basis of the Doppler effect (the Big Bang theory), while it is fully consistent with Hubble's quantum law.
 Vacuum fluctuations. |

 The pressure of the vacuum fluctuations on the parallel plates. The static Casimir effect. |
When the cosmological redshift was discovered, it was unknown that vacuum fluctuations existed and respectively, that the distribution of the electromagnetic waves is always accompanied by the energy dissipation due to the transformation of this energy into the inner energy of the vacuum. Therefore the only - as it then seemed - possible explanation was put forward: the Doppler effect. But not all scientists agreed to it, and the disputes continued. Some thought it to be connected with the Doppler effect, while others - including Edwin Hubble - thought that "the aging of light" ("tired light") happens, because ideal waves without dissipation simply do not exist.
and the redshift would be
At short distances - a full match with the Hubble's classical law
The dissipation of the photon energy per one oscillation:
After putting Hubble's law into its quantum form vn = nH0 it
becomes apparent that the cosmological redshift of the photon's frequency has
a quantum nature and depends only upon the number of oscillations per
traveled distance. That is to say, this is a quantum effect, where the wave's
energy is dissipated. There is no dependency on the number of oscillations in
the case of the Doppler effect. If the frequency decreases by the Hubble
constant with each new period, then such process presents wave energy
dissipation and not the Doppler effect.
Hubble's quantum law (quantum law of the
cosmological redshift) states that a photon's frequency decreases with each
new wave oscillation by a quantum amount equal to the Hubble constant,
vn = nH0,which is being observed as a redshift. Due to
the fact that the period of oscillation constantly increases, frequency
decreases with time t according to the law of exponent
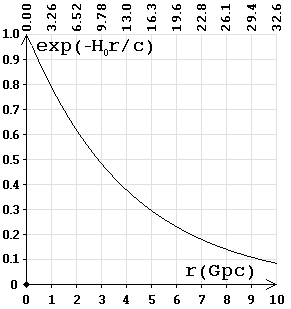 Frequency (energy) dependency on the distance. On top of the chart is the time (billion years). |
 Wavelength dependency on the distance. On top of the chart is the time (billion years) |
The graph shows that over 9.3 billion years (2.9 gigaparsecs)
the frequency is reduced by half. The frequency of the photon is directly
proportional to the energy; respectively,
«DAMPED OSCILLATIONS, the natural oscillations, the amplitude A
of which decreases with time t according to the law of the exponential
http://dic.academic.ru/dic.nsf/natural_science/4301/ЗАТУХАЮЩИЕ (In Russian)
The study of the work of Nobel Prize winners in 2011 on
the distant type Ia supernovae, attested that the observed redshift of the
frequency for both the near and distant galaxies coincides with
rather than z = 2, as assumed in the theory
of Universe's expansion, hence the brightness of the supernova is
lower.
«With displacements z = 2 ... speed
http://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Космологическое_красное_смещение
(In Russian)
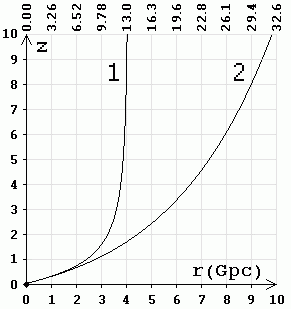 1 - according to the theory of the Universe expansion (the Doppler effect). 2 - according to the Hubble quantum law (by the method of "standard candles"). On top of the chart is the time (billion years). |
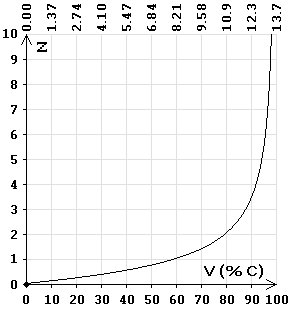 Speed dependence on the redshift by the Doppler effect (as percentage of the light speed). On top of the chart is the time (billion years). |
«In the works of the Nobel Prize winners in 2011 it was
discovered that the far away galaxies, the distance to which was calculated
by the Hubble's law, the type Ia supernova's have a brightness lower than the
one they were supposed to have. In other words, the distance to these
galaxies calculated by the method of the "standard candles" turns out to be
larger than the distance calculated on the basis of the previously set value
of the Hubble parameter. It was concluded that the Universe is not just
expanding, but that it is expanding with acceleration!»
http://hepd.pnpi.spb.ru/ioc/ioc/line%209-10-2011/n5.htm (In Russian)
«Thus, by studying distant from Earth supernovae's, the
winners found that those at least a quarter fainter than it had been
predicted by the theory, that means the stars are farther than determined
from the calculations.»
http://lebed.com/2011/art5913.htm (In Russian)
So studying distant supernovae's, the winners have found
that the distance calculated by the Doppler Effect does not correspond with
the actual distance to the stars. As of today Ia supernovae's are observed up
to z = 2. At z = 2, the distance calculated by the
Doppler effect, is 10.8 billion light-years (3.3 Gpc), and by the method
of "standard candles" 14.8 billion light-years (4.5 Gpc) redshift
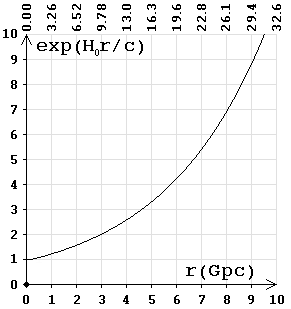
increases exponentially
«... the scale factor of the Universe behaves asymptotically like
this: a(t) ~ eH0t - the Universe will
expand exponentially, and this has not really been expected earlier. That is,
it is the accelerated expansion of the Universe, but before that, according
to the standard theory, it appeared that the Universe should expand with the
slowdown»
Lecture A.D.Linde. http://elementy.ru/lib/430484
(In Russian)
According to the method of "standard candles" the
following is established:
«... a(t) ~ eH0t ...
http://www1.jinr.ru/Pepan/2012-v43/v-43-3/01_dol.pdf
(In Russian)
During the studies of distant galaxies it was discovered
that cosmological redshift occurs according to the law of the exponentially
damped oscillations, in accordance with the Hubble's quantum law, not with
the Doppler effect, then - for the sake of the salvation of the Big Bang
theory and against all laws of physics - a 'miraculous' explanation was
invented: the accelerated expansion of the Universe due to dark energy
(force). But in this case, the speed of the young galaxies must be less than
the speed of the old ones, such as our galaxy, and, therefore, our time
should slow down more. Because of this, the observed (by us) duration of the
outbreaks of the distant supernovae's should decrease, and not increase.
«This way the galaxies, spectrum of which had the observed double
increase of the wavelength of light, had their supernova explosions extended
also by two times: from two weeks to four weeks.»
http://www.ritz-btr.narod.ru/compress.html (In Russian)
For each shift, red or purple (due to the Doppler effect,
or under the influence of gravity, etc.), always changes not only the
wavelength, but also the duration of the wave packets. This happens because
the number of periods of oscillation does not change and accordingly, the
duration of the wave packets (bursts) varies in direct proportion to the
wavelength
It is foolish to talk about the expansion with acceleration, if - no matter
where we look - according to the Doppler effect, the young (distant) galaxies
are moving faster than the old ones, that is to say that over time the speed
becomes less - braking is 22 km/s in a million years. At the same time -
in some magical way - the young galaxies right after the Big Bang happened to
be on the outskirts of the Universe. It turns out that in the first seconds
after the explosion, all matter was on the surface of a sphere with a radius
of 13.7 billion light-years and was moving away from the center with great
speed.
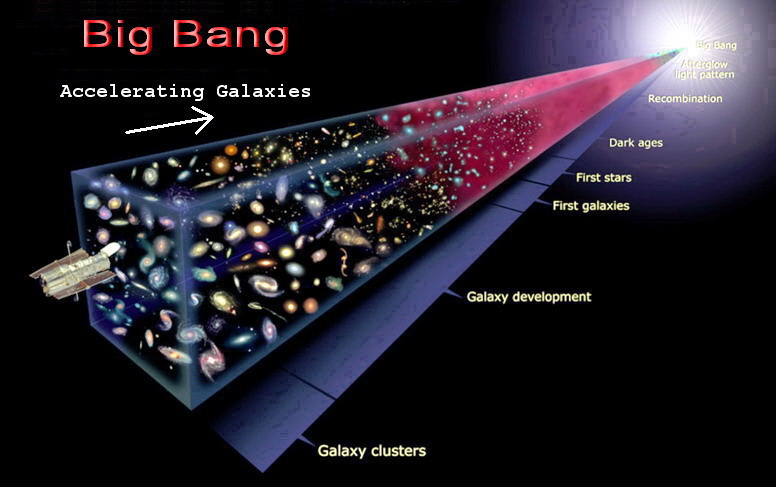
According to the theory of Universe
expansion, the younger the galaxy the faster it is moving away from us. That
is, the acceleration of the galaxies occurs in the direction of the very
first seconds after the Big Bang, and this acceleration is observed in any
direction from us, indicating the absence of any logic in the theory. It
turns out that the explosion is coming from the point of the Big Bang, and
conversely, the acceleration occurs on any side of us. The proponents of this
theory explain this absurdity by the fact that at the moment of the Big Bang
all laws of physics and logic can be broken, and therefore there is
"complete freedom of choice".
«At the point of the Big Bang and other singularities all the laws are
violated therefore God keeps complete freedom of choice of what was happening
in singularities and how the beginning of the Universe looked like.»
Also, the statement that the cosmic microwave background
radiation is associated with the Big Bang, contradicts logic, as in this case
it would have been observed on one side; on the side of the explosion, the
radiation source. For example, if somewhere a star explodes, one point would
be seen, the one where the explosion occurred. Radiation always comes from
the point of radiation. It is applicable to all sources, even those that are
more than 13 billion years old; they are also seen as points.
Due to the fact that on the basis of the theory of Universe expansion, the
distance calculated using the Doppler effect is wrong, the distant galaxies
appear to be small (compact), and type Ia supernovae have lower brightness.
For example, galaxy
«UDFj-39546284 is a compact galaxy, consisting of blue stars that have
existed 13.4 billion years ago, that is, approximately 380 million years after
the Big Bang. ... The galaxy has a redshift of z = 11.9.»
http://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/UDFj-39546284
(In Russian)
According to the Big Bang theory, at
z = 11.9 using the Doppler effect, the speed of the galaxy
is close to the speed of light and time passes very slowly, all processes are
slowed down z + 1 = 12.9 times. Accordingly,
it turns out that we have aged 380 million years, and galaxy has aged 29.5
million years after the Big Bang. But the formation of galaxies requires
about a billion years, and in such a short time the galaxy cannot be formed,
and if we consider that by the Doppler effect the distance to distant
galaxies is calculated incorrectly, time becomes negative.
«1 billion years - formation of the first galaxies.»
http://www.modcos.com/articles.php?id=105
(In Russian)
If vacuum field fluctuations exist, then in this vacuum
there also would be electromagnetic wave energy absorption - a wave's energy
transforms into fluctuation energy.
«At present it is ascertained that vacuum is not an "empty space". It is
certain material continuum with quite determined, but unclear properties. It
was confirmed by vacuum effects observation such as "zero-oscillations",
vacuum polarization, particle generation by electromagnetic interactions.
Therefore it is reasonable to suggest that physical vacuum could have real
own internal "friction" resistance due to its own small but real viscosity.
Thus, photons could interact with vacuum which could result in astronomical
redshift of the light.»
http://bourabai.narod.ru/shtyrkov/evolution.htm
(in Russian)
Waves are oscillations of a medium, as otherwise
diffraction and interference would not been observed. During the oscillations
there cannot be one hundred percent energy conversion, so the law of
attenuation is effective for all waves, due to dissipation by conversion of
one form of energy into another and back. No need to create myths, explaining
the cosmological redshift by the intervention of dark energy, "wedging the
galaxies off", since the usual formula of damped electromagnetic
oscillations, taking into account the quantum principles, allows accurate
calculation of the redshift for any distance.
«The chek-up showed that the data almost perfectly coincides with the
model of "tired light" and strongly disagrees with Friedmann's
model.»
http://www.vokrugsveta.ru/vs/article/6797/ (In Russian)
«Finally, after taking pictures of very distant objects (z of order 4)
with the space telescope "Hubble", when it was expected to see the separate
objects of the early Universe, close to the beginning of evolution, it became
clear, that the complex structures (galaxies) are seen again. It is clear
that it would take tremendous time for the formation of its structure,
compatible with the age of the Universe calculated for the Big Bang model.»
http://bourabai.narod.ru/shtyrkov/evolution.htm (In Russian)
«... there is no significant evolution of the metallicity of the GRB
host galaxies in the range 0 < z < 6.»
A report in the SAI 05.04.13.
http://sed.sao.ru/~vo/cosmo_school/presentations/Sokolov_paper.pdf
(In Russian)
One of the main tasks of the space telescope "Hubble" was
to see the border of the Universe, but it has not been found. Everywhere
there is roughly the same pattern of galaxies, which do not differ by age.
The Universe is homogeneous, isotropic, there is no evolution of metallicity
and no visible signs of the Big Bang.
Distance calculations by the method of "standard candles" showed that the
cosmological redshift is in exact accordance with the formulas of Hubble's
quantum law. In fact it turns out that the Nobel Prize in 2011 has been
awarded for the confirmation of the Hubble's quantum law.
Distribution of the quantum principles to the astrophysics helped to conclude
Hubble's quantum law, which, in contrast to the Doppler effect (the Big Bang
theory) allows correct calculation of the cosmological redshift for any
distance, as confirmed by the modern method of the "standard candles".
«Hubble's quantum law» in the «General Science Journal» (PDF)
Hubble's quantum law (Word)
Hubble's quantum law
(in Russian)
Braking of the space crafts caused by the vacuum fluctuations